| As of August 2020 the site you are on (wiki.newae.com) is deprecated, and content is now at rtfm.newae.com. |
CW308T-STM32F
| CW308T-STM32F | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Target Device | ST STM32F |
| Target Architecture | Cortex M0,M3,M4 |
| Hardware Crypto | Possible |
| Purchase Hardware |
Webstore, F1 Webstore, F3 Webstore, F4Webstore PCB |
| Design Files | OSH Park PCBs |
| Supported Apps | Simple Serial Enc/Auth |
| Programmer | ST-LINK/V2 |
| Status | Released |
Supported Devices
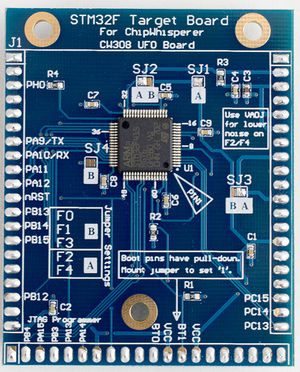
The STM32F board supports several STM32F devices in the TQFP-64 package. Various solder jumpers need to bet set to either the "A" or "B" position to select appropriate VCC supply for the different series. The following table summarizes examples of suitable devices:
| STM32F Series | Package | Device | Hardware AES | Tested | Jumper | Flash | SRAM | NAE P/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 | TQFP-64 | STM32F071RBT6 | No | Yes | B | 128KB | 16KB | NAE-CW308T-STM32F0 |
| F1 | TQFP-64 | STM32F100RBT6B | No | Yes | B | 128KB | 8KB | NAE-CW308T-STM32F1 |
| F2 | TQFP-64 | STM32F215RET6 | Yes | Yes | A | 512KB | 132KB | NAE-CW308T-STM32F2HWC |
| F3 | TQFP-64 | STM32F303RCT7 | No | Yes | B | 256KB | 40KB | NAE-CW308T-STM32F3 |
| F4 | TQFP-64 | STM32F415RGT6 | Yes | Yes | A | 1MB | 192KB | NAE-CW308T-STM32F4HWC |
| F4 | TQFP-64 | STM32F405RGT6 | No | Yes | A | 1MB | 192KB | NAE-CW308T-STM32F4 |
VCC-Int Supply
Several devices (F2, F4) have internal core voltage regulators. By default the CW308 board attempts to provide power for these pins, but the voltage may not be high enough to cause the internal regulator to disable itself. In this case you can use the VADJ regulator to ensure the internal regulator is disabled. See Targets with Internal Regulators for details.
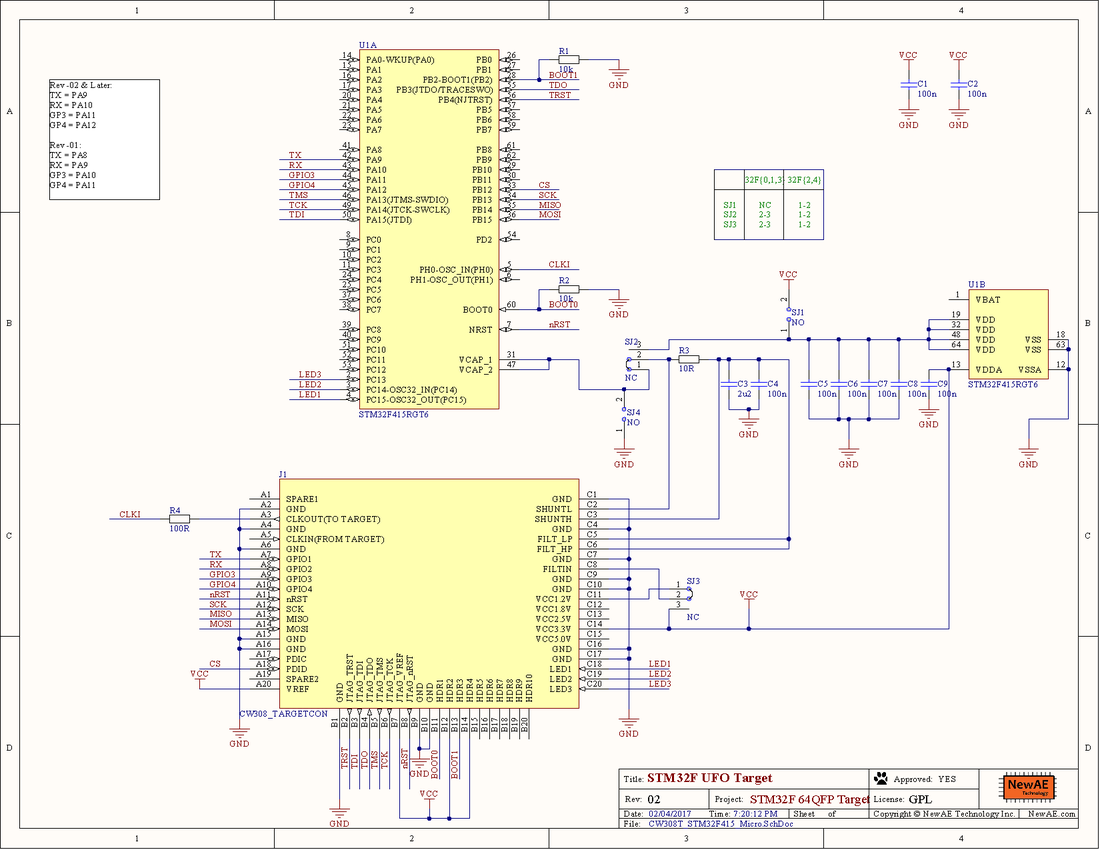
Pin-outs across TQFP Devices
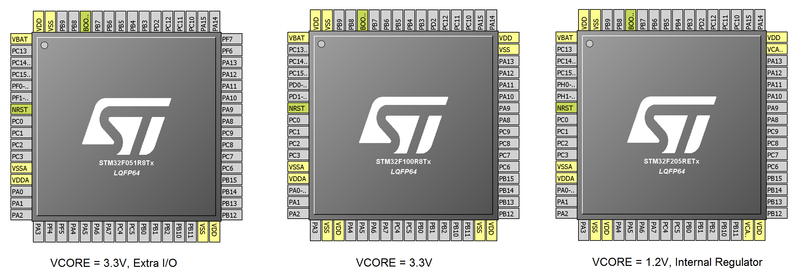
The following shows differences in pinouts between three groups of devices. The left-most is the STM32F051RB, which uses the same 3.3V VCORE as the STM32F1/F3. It has fewer VCC pins, so the I/O occupying that are VCC/GND pins on the STM32F1 (such as PF6/PF7) are tied to GND/VCC. The right-most part is the pinout of the STM32F2/F4. It has an internal regulator, where the VCAP pins are the output of this regulator (and input to the internal core logic).
Note for the devices with a 3.3V VCORE, you should not mount decoupling capacitors C5/C6/C7/C8. You will still get some leakage with those capacitors mounted, but a stronger signal is present without them.
Hardware AES
The STM32F21x, and STM32F41x/43x have hardware crypto modules (AES, DES, TDES) along with hardware hash (SHA1, MD5).
Programming Connection
ChipWhisperer Programmer via Bootloader
JTAG Programmer
The 20-pin JTAG port (J6 on CW308 Board) can be used with the ST-LINK/V2 which is a low-cost JTAG programmer.
It is also possible to use other JTAG programmers such as OpenOCD. The following command worked with an Olimex OpenOCD programmer and their OpenOCD for Windows software:
openocd -f path/to/board/files/cw308.cfg -c init -c targets -c "halt" -c "flash write_image erase path/to/firmware.hex" -c "verify_image path/to/firmware.hex" -c "reset run" -c shutdown
where the contents of cw308.cfg are
source [find interface/olimex-arm-usb-ocd-h.cfg] source [find target/stm32f4x.cfg] reset_config srst_only
Example Projects
SimpleSerial builds for each of the STM32Fx Devices. Each device is a separate HAL. These HAL modules have been copied from ST's HAL (not the CUBE) and greatly reduced in size by deleting unused files (such as headers for unused devices), and combining several C-source files into a single low-level C-file.
Building ST Example on Command Line
The regular firmware build process works with the STM32 devices. For example, to build `simpleserial-aes`, navigate to the folder `chipwhisperer\hardware\victims\firmware\simpleserial-aes` and run the following command on the command line:
make PLATFORM=CW308_STM32F0 CRYPTO_TARGET=TINYAES128C
If all goes well, this command will finish by printing the output file size and the platform:
Programming via ChipWhisperer Bootloader
These instructions have been updated for ChipWhisperer 5. If you're using and earlier version, see https://wiki.newae.com/V4:CW308T-STM32F/ChipWhisperer_Bootloader
The STM32Fx devices have a built-in bootloader, and the ChipWhisperer software as of 3.5.2 includes support for this bootloader.
Important notes before we begin:
- You MUST setup a clock and the serial lines for the chip. This is easily done by connecting to the scope and target, then running
default_setup():
import chipwhisperer as cw
scope = cw.scope
target = cw.target(scope)
scope.default_setup()
- On the STM32F1, you MUST adjust the clock frequency to 8MHz. The bootloader does not work with our usual 7.37 MHz clock frequency. This 8MHz frequency does not apply to the code that you're running on the device. Once you're done programming, you'll need to set the frequency back to F_CPU (likely 7.37MHz) For example:
scope.default_setup()
scope.clock.clkgen_freq = 8E6
#program target...
scope.clock.clkgen_freq = 7.37E6
#reset and run as usual
To access the bootloader you can perform these steps. They vary based on if you have a "Rev 02" board or a "Rev 03 or Later" board. The revision number is printed on the bottom side as part of the PCB part number (STM32F-03 is Rev -03 for example).
Rev -03 or Later
Run the following python code once you have the scope and target set up:
prog = cw.programmers.STM32FProgrammer
cw.program_target(scope, prog, "<path to fw hex file>")
If you get errors during the programming process:
- Retry the programming process with a lower baud rate:
prog = cw.programmers.STM32FProgrammer
cw.program_target(scope, prog, "<path to fw hex file>", baud=38400)
- If using a CW308 based STM, try mounting a jumper between the "SH-" and "SH+" pins at J16 (to the left of the SMA connector) on the UFO board. Retry programming with the jumper mounted.
Rev -02 Boards
The Rev -02 boards did not have all programming connections present. They require some additional steps:
- Setup the device as usual:
scope = cw.scope() target = cw.target(scope) scope.default_setup()
- Mount a jumper between the H1 and PDIC pins (again this is ONLY for the -02 rev).
- Reset the ARM device either by pressing the reset button (newer UFO boards only), or by toggling power:
import time scope.io.target_pwr = False time.sleep(1) scope.io.target_pwr = True
- Program the device:
prog = cw.programmers.STM32FProgrammer cw.program_target(scope, prog, "<path to fw hex file>")
- The device should program, it may take a moment to fully program/verify on larger devices.
- Remove the jumper between the H1/H2 pins.
- Reset the ARM device either by pressing the reset button (newer UFO boards only), or by toggling power:
import time scope.io.target_pwr = False time.sleep(1) scope.io.target_pwr = True
Running ST Example with ST-Link
If instead of using the bootloader, you want to use a ST-Link you can instead plug your programmer into the 20 pin JTAG connector (J6 on the UFO board):
Then, the details of this step will depend on your programmer. If you're using an ST-Link programmer, open the ST-Link utility and connect to the device:
Load your `.hex` file and program the device with the Program and Verify button:
After this, you're ready to go - you can use the ChipWhisperer terminal to talk to your target. You might need to reset the target before you do anything else.
Building and Debugging via ST's System Workbench
It's also possible to work on the example projects using ST's System Workbench IDE. This IDE also supports debugging, which is helpful for working out all the kinks in your firmware.
To build the ChipWhisperer examples in System Workbench:
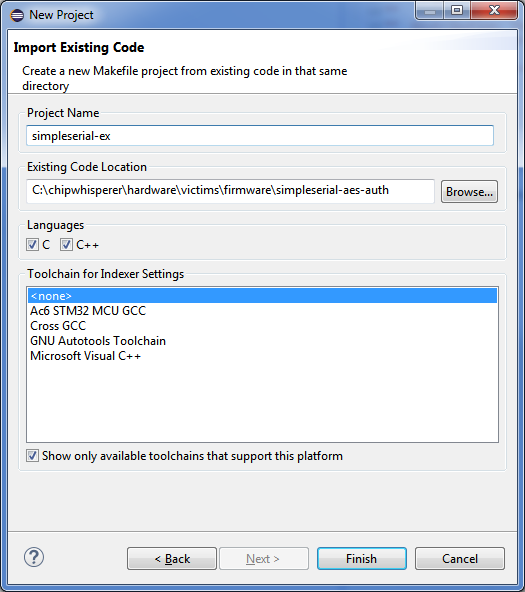
1. Create a Makefile Project with Existing Code and enter the firmware's location in Existing Code Location:
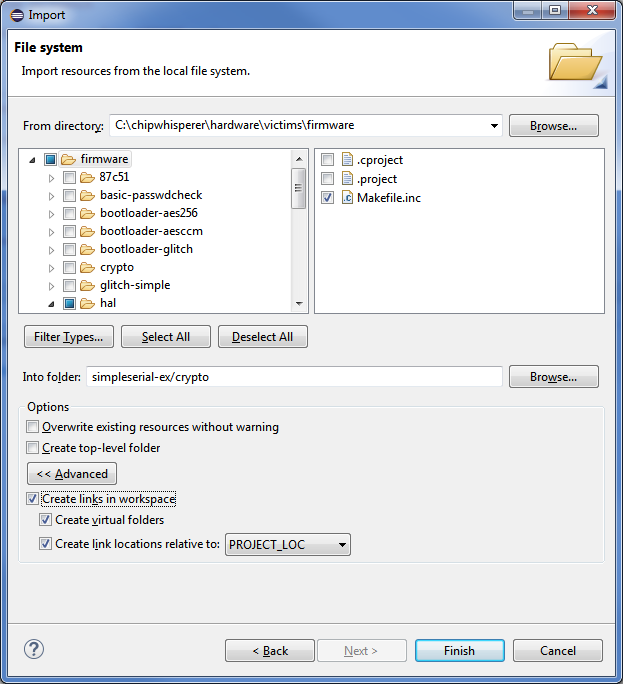
2. Link the external files into the project. To do this, under File > Import, select File System. In the `chipwhisperer\hardware\victims\firmware` directory, select all of the relevant files and folders (Makefile in base folder, Makefile in HAL folder, STM32Fx HAL folder). Ensure that make links to these files (instead of directly importing them):
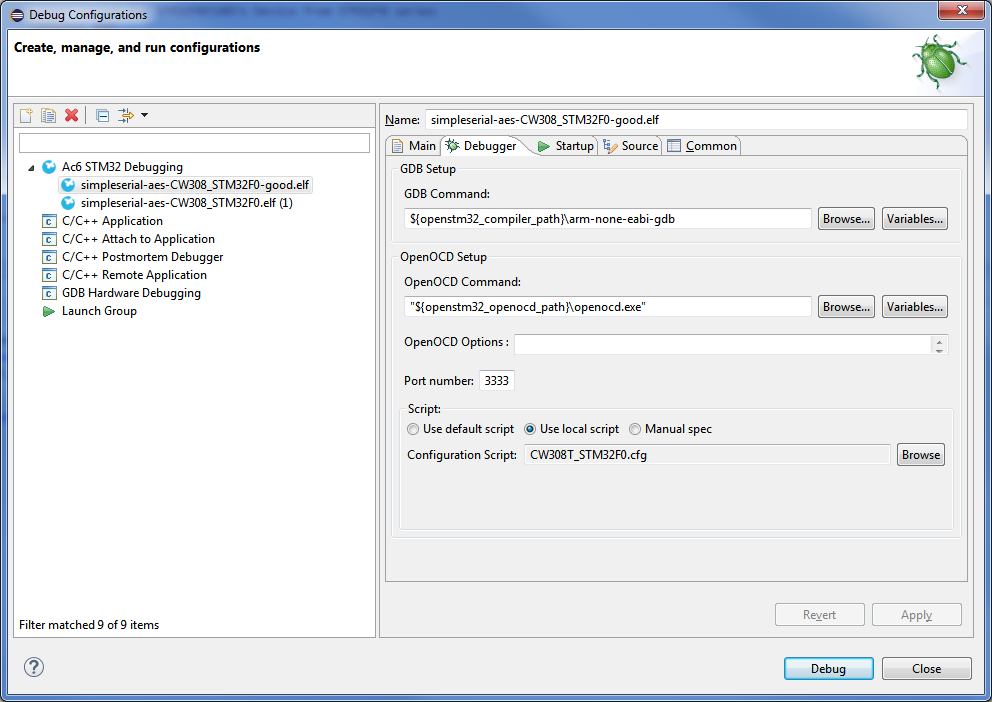
3. Set up the build command. In File > Properties, go to C/C++ Build and deselect 'Use default build command'. Enter the command you would normally enter on the command line:
4. Build the project and confirm that the build works from the output in the IDE console.
Then, if you want to set up debugging:
1. Find ST's list of debugging targets (check around `C:\STMicro\Ac6\SystemWorkbench\plugins\fr.ac6.mcu.debug_1.12.1.201703061527\resources\openocd\scripts\board`). Make a config file for your target. This file's contents should be something like (adjust for your board):
# This is an CW308T_STM32F0 board with a single STM32F071R8Tx chip. # Generated by System Workbench for STM32 source [find ../interface/stlink-v2-1.cfg] set WORKAREASIZE 0x2000 transport select "hla_swd" set CHIPNAME STM32F071R8Tx source [find ../target/stm32f0x_stlink.cfg] # use hardware reset, connect under reset reset_config srst_only srst_nogate
2. In Run > Debug Configurations, make a new Ac6 STM32 Debugging configuration. Under the 'Debugger' tab, select Use local script and select your custom script:
3. Enter debugging mode.
Caveat: the I/O register map in the debugger appears to use the last known device (ie: if you debugged an STM32F4 project before your Makefile project, it sticks with F4's registers). Check that the registers' addresses are correct before you trust them!