Template Attacks
Template attacks are a powerful type of side-channel attack. These attacks are a subset of profiling attacks, where an attacker creates a "profile" of a sensitive device and applies this profile to quickly find a victim's secret key.
Template attacks require more setup than CPA attacks. To perform a template attack, the attacker must have access to another copy of the protected device that they can fully control. Then, they must perform a great deal of pre-processing to create the template - in practice, this may take dozens of thousands of power traces. However, the advantages are that template attacks require a very small number of traces from the victim to complete the attack. With enough pre-processing, the key may be able to be recovered from just a single trace.
There are four steps to a template attack:
- Using a copy of the protected device, record a large number of power traces using many different inputs (plaintexts and keys). Ensure that enough traces are recorded to give us information about each subkey value.
- Create a template of the device's operation. This template notes a few "points of interest" in the power traces and a multivariate distribution of the power traces at each point.
- On the victim device, record a small number of power traces. Use multiple plaintexts. (We have no control over the secret key, which is fixed.)
- Apply the template to the attack traces. For each subkey, track which value is most likely to be the correct subkey. Continue until the key has been recovered.
Signals, Noise, and Statistics
Before looking at the details of the template attack, it is important to understand the statistics concepts that are involved. A template is effectively a multivariate distribution that describes several key samples in the power traces. This section will describe what a multivariate distribution is and how it can be used in this context.
Noise Distributions
Electrical signals are inherently noisy. Any time we take a voltage measurement, we don't expect to see a perfect, constant level. For example, if we attached a multimeter to a 5 V source and took 4 measurements, we might expect to see a data set like (4.95, 5.01, 5.06, 4.98). One way of modelling this voltage source is
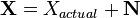
where 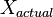 is the noise-free level and
is the noise-free level and 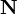 is the additional noise. In our example,
is the additional noise. In our example, 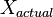 would be exactly 5 V. Then,
would be exactly 5 V. Then, 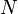 is a random variable: every time we take a measurement, we can expect to see a different value. Note that
is a random variable: every time we take a measurement, we can expect to see a different value. Note that 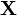 and
and 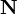 are bolded to show that they are random variables.
are bolded to show that they are random variables.
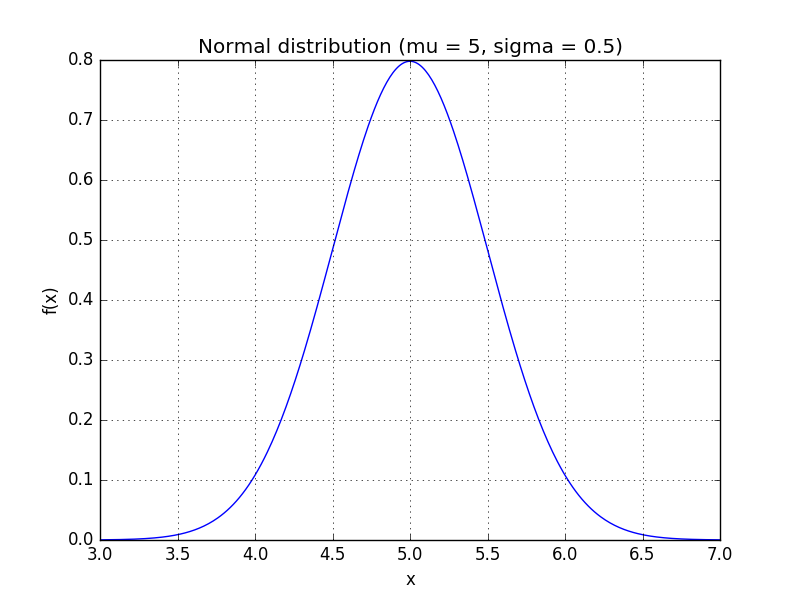
A simple model for these random variables uses a Gaussian distribution (read: a bell curve). The probability density function (PDF) of a Gaussian distribution is
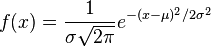
where 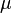 is the mean and
is the mean and 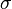 is the standard deviation. For instance, our voltage source might have a mean of 5 and a standard deviation of 0.5, making the PDF look like:
is the standard deviation. For instance, our voltage source might have a mean of 5 and a standard deviation of 0.5, making the PDF look like:
We can use the PDF to calculate how likely a certain measurement is. Using this distribution,
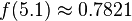
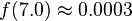
so we're very unlikely to see a reading of 7 V. We'll use this to our advantage in this attack: if 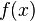 is very small for one of our subkey guesses, it's probably a wrong guess.
is very small for one of our subkey guesses, it's probably a wrong guess.
Multivariate Statistics
The 1-variable Gaussian distribution works well for one measurement. What if we're working with more than one random variable?
Suppose we're measuring two voltages that have some amount of noise on them. We'll call them 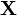 and
and 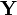 . As a first attempt, we could write down a model for
. As a first attempt, we could write down a model for 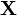 using a normal distribution and a separate model for
using a normal distribution and a separate model for 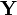 using a different distribution. However, this might not always make sense. If we write two separate distributions, what we're saying is that the two variables are independent: when
using a different distribution. However, this might not always make sense. If we write two separate distributions, what we're saying is that the two variables are independent: when 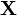 goes up, there's no guarantee that
goes up, there's no guarantee that 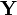 will follow it.
will follow it.
Multivariate distributions let us model multiple random variables that may or may not be correlated. In a multivariate distribution, instead of writing down a single variance 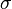 , we keep track of a whole matrix of covariances. For example, to model three random variables (
, we keep track of a whole matrix of covariances. For example, to model three random variables (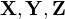 ), this matrix would be
), this matrix would be
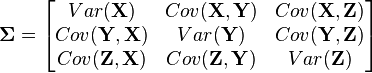
Also, note that this distribution needs to have a mean for each random variable:
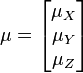
The PDF of this distribution is more complicated: instead of using a single number as an argument, it uses a vector with all of the variables in it (![\mathbf{x} = [x, y, z, \dots]^T](/images/math/9/2/c/x92c0cda2bde551dd57b06ef9cf59e38c.png.pagespeed.ic.Z2xK6NS_xs.png) ). The equation for
). The equation for 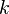 random variables is
random variables is
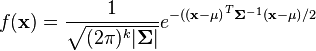
Don't worry if this looks crazy - the SciPy package in Python will do all the heavy lifting for us. As with the single-variable distributions, we're going to use this to find how likely a certain observation is. In other words, if we put 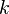 points of our power trace into
points of our power trace into 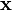 and we find that
and we find that 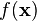 is very high, then we've probably found a good guess.
is very high, then we've probably found a good guess.
Creating the Template
A template is a set of probability distributions that describe what the power traces look like for many different keys. Effectively, a template says: "If you're going to use key 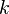 , your power trace will look like the distribution
, your power trace will look like the distribution 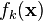 ". We can use this information to find subtle differences between power traces and to make very good key guesses for a single power trace.
". We can use this information to find subtle differences between power traces and to make very good key guesses for a single power trace.
Number of Traces
One of the downsides of template attacks is that they require a great number of traces to be preprocessed before the attack can begin. This is mainly for statistical reasons. In order to come up with a good distribution to model the power traces for every key, we need a large number of traces for every key. For example, if we're going to attack a single subkey of AES-128, then we need to create 256 power consumption models (one for every number from 0 to 255). In order to get enough data to make good models, we need tens of thousands of traces.
Note that we don't have to model every single key. One good alternative is to model a sensitive part of the algorithm, like the substitution box in AES. We can get away with a much smaller number of traces here; if we make a model for every possible Hamming weight, then we would end up with 17 models, which is an order of magnitude smaller. However, then we can't recover the key from a single attack trace - we need more information to recover the secret key.
Points of Interest
Our goal is to create a multivariate probability describing the power traces for every possible key. If we modeled the entire power trace this way (with, say, 3000 samples), then we would need a 3000-dimension distribution. This is insane, so we'll find an alternative.
Thankfully, not every point on the power trace is important to us. There are two main reasons for this:
- We might be taking more than one sample per clock cycle. (Through most of the ChipWhisperer tutorials, our ADC runs four times faster than the target device.) There's no real reason to use all of these samples - we can get just as much information from a single sample at the right time.
- Our choice of key doesn't affect the entire power trace. It's likely that the subkeys only influence the power consumption at a few critical times. If we can pick these important times, then we can ignore most of the samples.
These two points mean that we can usually live with a handful (3-5) of points of interest. If we can pick out good points and write down a model using these samples, then we can use a 3D or 5D distribution - a great improvement over the original 3000D model.
Picking POIs
TODO; want to write tutorial first
Analyzing the Data
How to find the covariance matrices
Using the Template
Apply the template by measuring more traces
Finding the Key
How to use the template to narrow down the possibilities
Attack Time
Shouldn't take long to attack