| As of August 2020 the site you are on (wiki.newae.com) is deprecated, and content is now at rtfm.newae.com. |
Difference between revisions of "CW506 Advanced Breakout Board"
(→SW4 (Target Disconnect)) (Tag: VisualEditor) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! | ! | ||
| − | !3.3V Logic | + | !scope="row" colspan="2"|3.3V Logic |
| − | + | !scope="row" colspan="5"|VCC-IO Logic | |
| − | !VCC-IO Logic | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
!SW4 Setting | !SW4 Setting | ||
Revision as of 04:25, 7 June 2016
Contents
Background
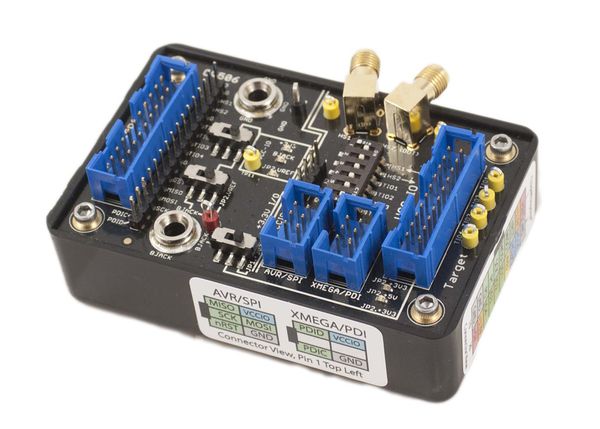
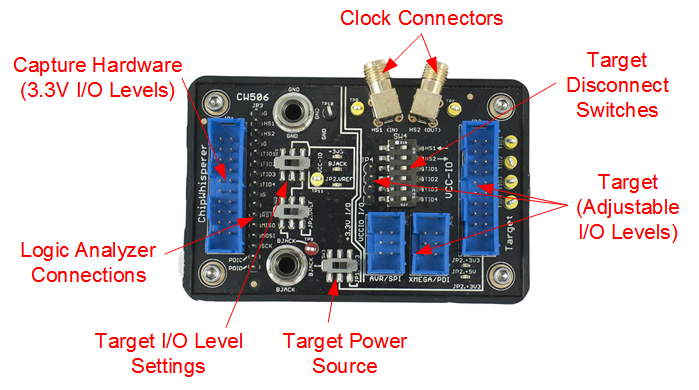
The CW506 is a simple but powerful breakout board for devices using NewAE Technology's 20-Pin Connector standard. Almost all of our target boards and capture hardware feature this connector, making the breakout board widely applicable to our product line.
The breakout board features a variety of voltage translators, test points, connectors, and switches that makes it simple to interface various test equipment and target devices together. This includes both connecting other lab equipment, along with connecting ChipWhisperer capture hardware to your own targets.
Connection Routing
The following shows the routing of various connections on the breakout board:
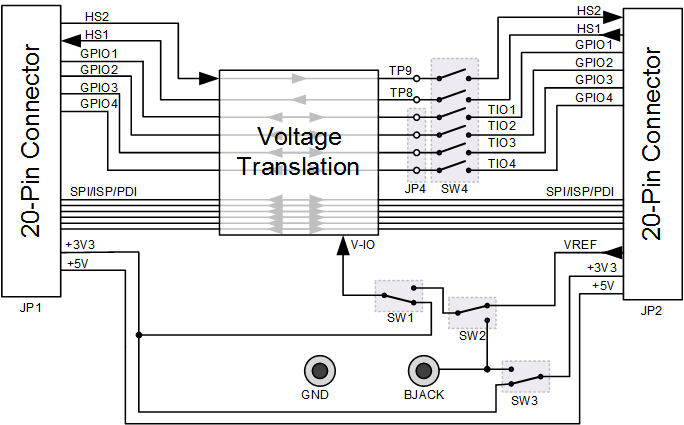
Voltage Translation
The voltage translation is done with three different parts:
- SN74LVC1T45DBVT for high-speed clock lines (unidirectional, approx 200 Mbps max speed, 1.65V - 5.5V)
- PI4ULS5V201TAEX for GPIO1/2 (bidirectional, approx 20 Mbps max speed, 1.2V - 5.5V)
- GTL2003PW for GPIO2/3 + Others (bidirectional, 1.0V - 5.5V)
Note the clock translators limit lower operating voltage, if not using HS1 or HS2 you can safely use this board down to 1.2V. The maximum speed of the voltage translators varies with different output voltages, see datasheet for details.
The VCCIO net on the board defines what logic level the target (i.e., the signals on the jumpers and headers on the right side of the board) section operates at. There is a vertical double-line on the breakout board, everything on the right side of the double-line operates at VCC-IO levels.
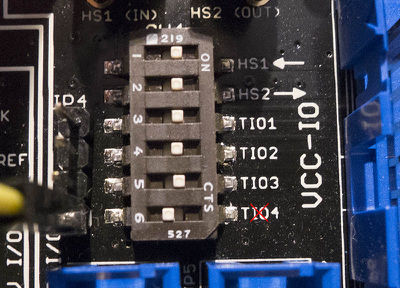
SW4 (Target Disconnect)
A DIP switch can be used to disconnect certain pins of the 20-pin header. The DIP switch has small text marked "ON", when the DIP switch is moved to this position the 20-pin connector is ENABLED.
The following shows an example where we've disconnected GPIO4 (the trigger) from our target device, and am feeding an external trigger in with the header (JP4) to the left of the DIP switch. This new trigger signal will be routed to the attached ChipWhisperer, and can be used instead of the trigger coming from the target device. Notice the DIP switch for TIO4 (GPIO4/IO4) is set to the LEFT, and the rest are set to the RIGHT (ON).
The following summarizes the connection for different SW4 settings. Note the 20-pin connector and the test-points to the right of that connector (marked TIO1, TIO2, TIO3, TIO4) are the only things disconnected.| 3.3V Logic | VCC-IO Logic | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW4 Setting | JP1 (Left 20-Pin) | JP3 | JP4 | JP5/JP6 | JP2 (Right 20-Pin) | TIO1-TIO4 Test Points | TP7/TP8, SMA Connectors |
| OFF | TIO1-TIO4 | ☑ | ☑ | ||||
| ON | TIO1-TIO4 | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ||
| OFF | HS1-HS2 | ☑ | ☑ | ||||
| ON | HS1-HS2 | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | |||
| ? | SPI/PDI/Other | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | |||
VCC-IO Settings
JP2.+3v3 Settings
Use Cases
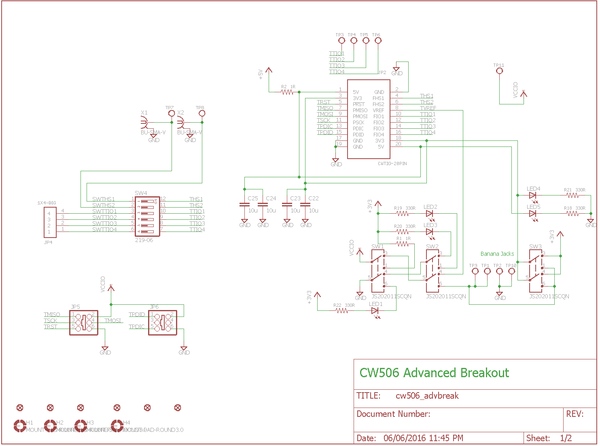
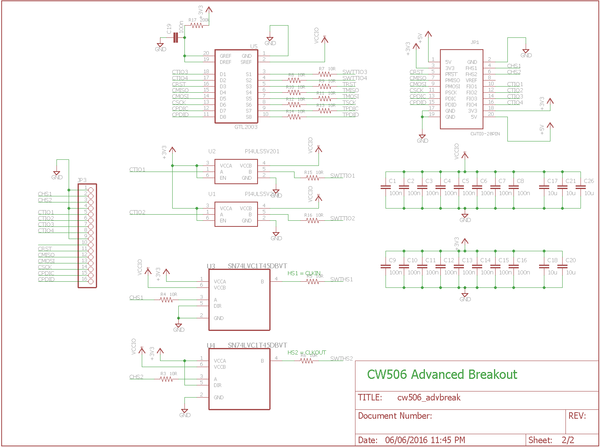
Schematic
The schematic is available in two formats - PDF and schematic images. Click the images for full resolution.